نمایش نتیجه 341 تا 350 از 1523 نتیجه یافت شده برای LT:
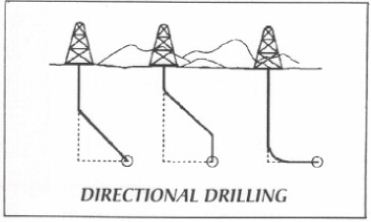
n:1. intentional deviation of a wellbore from the vertical. Although well bores are normally drilled vertically, it is sometimes necessary or advantageous to drill at an angle from the vertical. Controlled directional drilling makes it possible to reach subsurface areas laterally remote from the point where the bit enters the earth. It often involves the use of deflection tools. 2. a technique of river crossing in pipeline construction in which the pipe is buried under the riverbed at very much greater than those of conventional crossings. With this technique, a hole in the form of an inverted arc is drilled beneath the river, and the made-up pipeline is pulled through it.
n: The intentional deviation of a wellbore in order to reach an objective some distance from the rig.
drilling the wellbore in a planned angle of deviation or trajectory.
حفاری جهت دار
n: a logging method that records drift angle, or deflection from the vertical, and direction of the drift. A singleshot directional-survey instrument makes a single photograph of a compass reading of the drift direction and the number of degrees the hole is off vertical. A multi shot survey instrument obtains numerous readings in the hole as the device is pulled out of the well. See directional drilling.
n: A method of measuring the inclination and direction of the wellbore by using a downhole instrument. The well must be surveyed at regular intervals to plot its course accurately.
a measurement of the well path that records the inclination and azimuth of the wellbore using a compass or other device.
n: a tool that, when lowered into the wellbore, makes a photographic record of the angle and drift of the wellbore;that is, it records the number of degrees the hole is off vertical and the direction in which it is off vertical. Several types of instrument are available;some are capable of photographing only a single record - single-shot survey instrumentswhereas others are capable of making several records in one run - multishot survey instruments.
n: a suspension of extremely fine particles in a liquid (such as colloids in a colloidal solution).
n: Subdivision of aggregates. Dispersion increases the specific surface of the particle, which results in an increase in viscosity and gel strength.
a mixture of a internal phase of solids, droplets or bubbles that stay relatively suspended in a continuous fluid.
پراکندگی
n: in oilwell cementing, the fluid. usually drilling mud or salt water, that is pumped into the well after the cement is pumped into it to force the cement out of the casing and into the annulus.
n: A kind of multiple cement method in which the gate plug reaches the collar under the promotation of the displacement fluid
n: a well into which salt water or spent chemical is pumped, most commonly part of a saltwater-disposal system.
a well into which fluids such as produced water and some liquid wastes can be injected. It is in a non hydrocarbon, non-fresh water sand and is not connected to the hydrocarbon bearing formation.
چاه دفعی
n: an electrical device designed to reduce voltage from primary distribution levels, usually 7,200 or 12,400 volts, to utilization voltages of 480, 240, or 120 volts. See power transfornlet:
a: Having a valency of two. When a salt is referred to as divalent, the metal ion has a valency of two.
a material that forces acid to enter another zone by having a higher viscosity or building a filter cake.