نمایش نتیجه 441 تا 450 از 1523 نتیجه یافت شده برای LT:
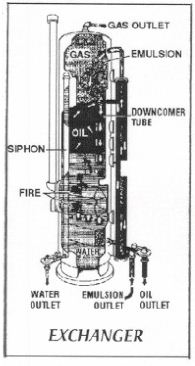
n: a piping arrangement that permits heat from one fluid to be transferred to another fluid as they travel counter currently to one another. In the heat exchanger of an emulsion-treating unit, heat from the outgoing clean oil is transferred to the incoming well fluid, cooling the oil and heating the well fluid. In the heat exchanger of a glycol dehydration unit, heat from the hot lean glycol flows through the inner flow tube in the opposite direction of the cool rich glycol, which flows through a shell built around the tube.
localized and subsurface corrosion in zones often parallel to the surface that result in leaving thin layers of uncorroded metal resembling the pages of a book.
n: a siliceous volcanic rock that is finely ground and subjected to extreme heat. The resulting release of water leaves the rock particles considerably expanded and thus more porous. Expanded perlite is sometimes used in cement to increase its yield and decrease its density without an appreciable effect on its other properties.
n: a siliceous ash rock which is grinded and processed under the hyperthermic situation,usually used to improve the mud making rate of the cement slurry and decline the density
n: a multiplying factor used when calculating gas flow rate. This factor corrects for the reduction in fluid density that a compressible fluid experiences when it passes through an orifice as a result of the increased fluid velocity and the decreased static pressure. Also called expansibility factor.
n: a loop built into a pipeline to allow for expansion and contraction of the line.
n: a risk analysis process that multiplies expected gain or loss of a decision by its probability of occurrence and averages all possible outcomes to choose the action with the highest expected benefit.
n: when explosives are used to fracture a formation. At the moment of detonation, the explosion furnishes a source of high-pressure gas to force fluid into the formation. The rubble prevents fracture healing, making the use of proppants unnecessary. Compare hydraulic fracturing.
one of several techniques used to break the rock in the near well area. It was an early stimulation method. Fractures formed in this method are short. Although still used, its best application is in perf breakdown and overcoming some near well damage.
n pi: the limits (based on time of exposure, concentration of material, means of contact, and material toxicity) of worker exposure to hazardous materials without ill effect. Exceeding exposure limits set for various materials can result in temporary health problems, chronic illness, acute illness, or death.
n: the solid stratum granulosum which forms on the borehole wall after the fluid dehydrations in the layer with cellules
filtration control established on the surface of the wellbore by particles large enough to bridge on the entry of the pores.
n: the multipointed slip whose length is larger than the length of long casing slip