نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 487 نتیجه یافت شده برای drilling fluid:
n: The physicist A. E. Boycott found that the blood cell deposits faster when test tube deflects, especially 40°-50°, than when test tube is vertical. The same situation will be found in the drilling fluid in the horizontal well. That is why people call this
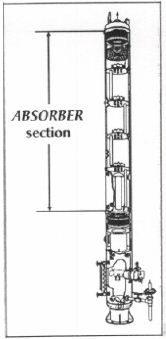
n: 1. A vertical, cylindrical vessel that recovers heavier hydorcarbons from a mixture of predominantly lighter hydrocarbons. Also called absorption tower. 2. A vessel in which gas is dehydrated by being bubbled through glycol. See absorb.
n: It refers to the row tube holding thezinky
material during the analysis of drilling fluid. Used to survey the content
of H2S.
a vertical, cylindrical vessel that recovers heavier (longer carbon chain) hydrocarbons from a mixture of lighter hydrocarbons.
ظرف جذب
n: The treating chemical
loss during manufacturing or purifying drilling fluid agent according to the principle of absorption.
n: CH2=CHONH2, a kind of organic amine, is a materal for hydro polyacrylamide coagulant of drilling fluid.
n: CH2=CHCN, a kind of organic compound, colourless and fluxionary liquid. The vapor is toxic. It is the important material for coagulant of drilling fluid.
n: The circulating fluid for drilling. It content the drilling fluid both in the wellbore and surface circulating system.
n: 1. in general, a substance added in small amounts to a larger amount of another substance to change some characteristic of the latter. In the oil industry, additives are used in lubricating oil, fuel, drilling mud, and cement. 2. in cementing, a substance added to cement to change its characteristics to satisfy specific conditions in die well. A cement additive may work as an accelerator, retarder, dispersant, or other reactant.
n: The agent put into the drilling fluid in order to change some performances of the drilling fluid or slurry.
a compound incorporated into a gas, liquid, or solid system to alter the properties for a particular purpose.
افزودنی
n: The number of treating chemical of drilling fluid that the adsorbent can adsorb when the adsorption is under balance.
n: The number of treating chemical of drilling fluid that the adsorbent can adsorb when the adsorption is under balance.
n: Made by adding gas into common water base drilling fluid. Mainly used to protect circulation loss in low pressure formation and leakage zone.