نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 23 نتیجه یافت شده برای electrolyte:
n: 1. one of two electrodes in an electrolytic cell, represented as the positive terminal of a cell. 2. in cathodic protection systems, the protected structure that is representative of the cathode and is protected by having a conventional current flow from an anode to the structure through the electrolyte.
the negative site of a corrosion cell. Reduction reactions are typical.
cracking of a metal under combined action of tensile stress and corrosion in the presence of chlorides and an electrolyte (NACE). Starts at a pit, scratch or notch. Crack proceeds primarily along grain boundaries. The cracking process is accelerated by ch
n: 1. the ability to transmit or convey (as heat or electricity). 2. an electricallogging measurement obtained from an induction survey, in which eddy currents produced by an alternating magnetic field induce in a receiver coil a voltage proportionate to the ability of the formation to conduct electricity. See induction log.
n: Measure of the quantity of electricity transferred across unit area per unit potential per unit time. It is the reciprocal of resistivity. Electrolytes may be added to a fluid to alter its conductivity.
رسانایی ویژه
n: a commonly used nonpolarising electrode used in corrosion control to measure the electrical potential of a metal structure to a surrounding electrolyte to determine the potential for corrosion damage or to monitor the effectiveness of existing control measures. See half-cell.
potential of a corroding surface in an electrolyte relative to a reference electrode under open-circuit conditions.
n: a primary cell, such as a flashlight battery, in which the electrolyte is a paste. The term dry" is misleading, because moisture is necessary for the electrolyte to function.
n: a conductor of electric current as it leaves or enters a medium such as an electrolyte, a gas, or a vacuum.
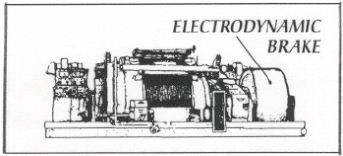
n: an electrochemical process by which metal settles out of an electrolyte that contains the metals ions and is then deposited at the cathode of the cell. electrodynamic brake n: a device mounted on the end of the drawworks shaft of a drilling rig. The electrodynamic brake (sometimes called a magnetic brake) serves as an auxiliary to the mechanical brake when pipe is lowered into a well. The braking effect in an electrodynamic brake is achieved by means of the interaction of electric currents with magnets, with other currents, or with themselves.
n: 1. a chemical that, when dissolved in water, dissociates into positive and negative ions, thus increasing its electrical conductivity. See dissociation. 2.the electrically conductive solution that must be present for a corrosion cell to exist.
n: A substance that dissociates into charged positive and negative ions when in solution or a fused state. This electrolyte will then conduct an electric current. Acids, bases, and salts are common electrolytes.
a material that, when dissolved in water, causes or increases the fluids’ electrical conductivity.
n: a list of elements arranged in order of activity (tendency to lose electrons). The following metals are so arranged: magnesium, beryllium, aluminum. zinc, chromium, iron, cadmium, nickel, tin. copper, silver, and gold. If two metals widely separated in the list (e.g., magnesium and iron) are placed in an electrolyte and connected by a metallic conductor, an electromotive force is produced. See corrosion.





