نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 16 نتیجه یافت شده برای hydraulic pump:
n: any method used to raise oil to the surface through a well after reservoir pressure has declined to the point at which the well no longer produces by means of natural energy. Sucker rod pumps, gas lift, hydraulic pumps, and submersible electric pumps are the most common means of artificial lift.
one of several methods that provide pressure assistance to increase flow from a well. The most common systems lighten (decrease density) of the flowing fluid (gas lift),or remove all or part of the liquid head from the reservoir (beam and electric submer
استخراج مصنوعی
n: any of the rod pumps, high-pressure liquid pumps, or centrifugal pumps located at or near the bottom of the well and used to lift the well fluids. See centrifugal pump. hydraulic pumping. submersible pump. sucker rod pumping.
n: The dynamic or hydraulic pump installed in hi-pressure liquid storage tank.
n: an electric or hydraulic pump on an accumulator that pumps hydraulic fluid under high pressure to the blowout preventers so that they may be closed or opened.
n: the equipment for transporting and using coiled tubing, including a reel for the coiled tubing, an injector head to push the tubing down the well, a wellhead blowout preventer stack, a power source (usually a diesel engine and hydraulic pumps),and a control console. A unique feature of the unit is that it allows continuous circulation while it is being lowered into the hole. A coiled tubing unit is usually mounted on a trailer or skid.
n: a type of downhole hydraulic pump that is attached to the end of tubing;the tubing must be pulled to service the pump. See hydraulic pump. Compare free pump.
n: a type of downhole hydraulic pump that moves in and out of the well by means of circulating fluids. See hydroulic pump. Compare fixed pump.
n: a specialised form of hydraulic pump, used in artificial lift. whose main working parts are nozzle, throat, and diffuser. The nozzle converts the highpressure, low-velocity energy of the power fluid to high-velocity, low-pressure energy. The power fluid is then mixed with the lowpressure pump intake fluid in the throat to produce a low-pressure stream with a velocity less than that of the nozzle exit, but a high velocity, nevertheless. The velocity energy of this mixed stream is then converted to static pressure in the diffuser to provide the pressure necessary to lift fluid from the well. The power fluid may be either oil or water.
n: a device that lifts oil from wells without the use of sucker rods. See hydraulic pumping.
an artificial lift system that is powered by injected fluid (usually water),that powers a pump similar to the rotating pump used in electrical submersible pumps.
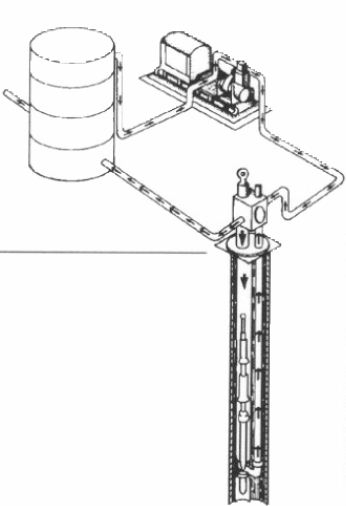
n: a method of pumping oil from wells by using a downhole pump without sucker rods. Subsurface hydraulic pumps consist of two reciprocating pumps coupled and placed in the well. One pump functions as an engine and drives the other pump (the production pump). The downhole engine is usually operated by clean crude oil under pressure (power oil) that is drawn from a power-oil settling tank by a triplex plunger pump on the surface. If a single string of tubing is used, power oil is pumped down the tubing string to the pump, which is seated in the string, and a mixture of power oil and produced fluid is returned through the casing-tubing annulus. If two parallel strings are used, one supplies power oil to the pump while the other returns the exhaust and produced oil to the surface. A hydraulic pump may be used to pump several wells from a central source and has been used to lift oil from depths of more than 10,000 feet (3,048 metres).





