نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 24 نتیجه یافت شده برای improved recovery:
n: a method of improved recovery in which alkaline chemicals such as sodium hydroxide are injected during a water flood or combined with polymer flooding. The chemicals react with the natural acid present in certain crude oils to form surfactants within the reservoir. The surfactants enable the water to move additional quantities of oil from the depleted reservoir. Compare chemical flooding, polymer flooding, water flooding.
Developed reserves are expected to be recovered from existing wells including reserves behind pipe. Improved recovery reserves are considered developed only after the necessary equipment has been installed, or when the costs to do so are relatively minor.
n: in improved recovery, the amount of coke available for in situ combustion. measured in pounds per cubic foot of burned area. Coke is formed by thermal cracking and distillation in the combustion zone. The amount of available coke depends on the composition of the reservoir cn* oil.
n: the introduction of artificial drive and displacement mechanisms into a reservoir to produce a portion of the oil unrecoverable by primary recovery methods. See enhanced oil recovery.
n: a method of improved recovery in which heat is generated within the reservoir by injecting air and burning a portion of the oil in place. The heat of initial combustion cracks the crude hydrocarbons, vaporises the lighter hydrocarbons, and deposits the heavier hydrocarbons as coke. As the fire moves from the injection well in the direction of producing wells, it bums the deposited coke, releases hot combustion gases, and converts connate water into steam. The vaporised hydrocarbons and the steam move ahead of the combustion zone, condensing into liquids as they cool and moving oil by miscible displacement and hot waterflooding. Combustion gases provide additional gas drive. Heat lowers the viscosity of the oil, causing it to flow more freely. This method is used to recover heavy, viscous oil. Also called fire flooding.
احتراق درجا
n: the spacing and pattern of wells in an improved recovery project, determined from the location of existing wells, reservoir size and shape, the cost of drilling new wells, and the oil recovery expected from various patterns. Common injection patterns include line drive, five spot, seven spot, nine spot, and peripheral.
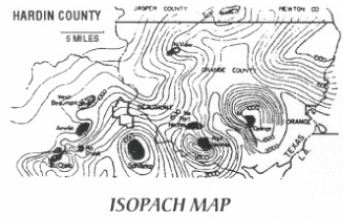
n: a geological map of subsurface strata showing the various thicknesses of a given formation as a series of contours. It is widely used in calculating reserves and in planning improved recovery projects.
نقشه ی هم ضخامت
n: the ratio of the mobility of a driving fluid (water or a chemical solution at residual oil saturation to the mobility of the driven fluid (oil) at connate water saturation. The mobility ratio affects the sweep efficiency of an improved recovery project.
a comparison of the ability of a fluid to move through another fluid or to displace the fluid.
نسبت تحرک
n: the use of waterflooding or gas injection to provide additional formation pressure to supplement and to conserve natural reservoir drives. Although commonly begun during primary production, pressure maintenance is a form of improved recovery. See improved recovery, secondary recovery.
روش حفظ فشار
Reserves subcategorized as producing are expected to be recovered from completion intervals which are open and producing at the time of the estimate. Improved recovery reserves are considered producing only after the improved recovery project is in operat