نمایش نتیجه 191 تا 200 از 581 نتیجه یافت شده برای lb:
n: circulating fluid, one function of which is to lift cuttings out of the wellbore and to the surface. It also serves to cool the bit and to counteract downhole formation pressure. Although a mixture of barite, clay, water, and other chemical additives is the most common drilling fluid, wells can also be drilled by using air, gas, water, or oil-base mud as the drilling mud. Also called circulating fluid, drilling mud. See mud.
n: The fluid circulated through the drill string and up the annulus back to surface under normal drilling operations. Usually referred to as mud.
گل حفاری
n: a specially compounded liquidcirculated through the wellbore during rotary drilling operations. See drilling fluid, mud.
n: A circulating fluid used in rotary drilling to perform any or all of various functions required in the drilling operation.
the fluid, water, oil or gas based, that is used to establish well control, transport cuttings to the surface, provides fluid loss control, lubricates the string and cools the bottom hole assembly.
گل حفاری
n: the measure used to develop the drilling speed , gurrantee the wellbore quality and prevent borehole problems and accident
روش حفاری
n: the degree of superior and inferior of the drilled wellbore ,mainly including the wellbore quality ,core recovery, cement job quality and complete quality
n: the continuation of drilling operations while maintaining a seal at the top of the wellbore to prevent the well fluids from blowing out.
n: refer to under balance pressure drilling
n: 1. the means by which a machine is given motion or power, or by which power is transferred from one part of a machine to another.2. the energy of expanding gas, inflowing water, or other natural or artificial mechanisms that forces crude oil out of the reservoir formation and into the wellbore. v: to give motion or power.
n: the drill pipe from which drilling mud has been emptied as it is pulled out of the wellbore.
n: there is no fluid blowing out from the drill string affter the disconnection
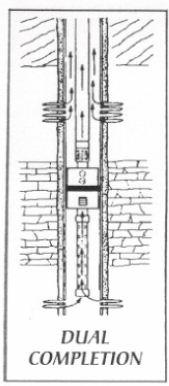
n: a single well that produces from two separate formations at the same time. Production from each zone is segregated by running two tubing strings with packers inside the single string of production casing, or by ruunign one tubing string with a packer through one zone while the other is produced through the annulus. In a miniaturised dual completion, two separate 4.5-inch (11.4-centimetre) or smaller casing strings are run and cemented in the same wellbore.
n: a completion method in which two hydrocarbon reservoirs with different pressure in the same well
two pay zones in the same well that produce up independent flow paths in the same well.
n: a log designed to provide the resistivity measurements necessary to estimate the effects of mud filtrate invasion into the formation surrounding the wellbore so that more reliable values for the the formation resistivity may be obtained. The resistivity curves on this log are made by deep-, medium-, and shallow-investigation induction. Visual Observation of the dual induction focused log can give valuable information regarding invasion, porosity, and hydrocarbon content. The three curves on the log can be used to correct for deep invasion and obtain a better value for formation resistivity. Compare induction survey.
n: the annular between the wall and the epitheca of pipe is heterogeneous because the axis of pipe and the axis of wellbore are misalignment





