نمایش نتیجه 291 تا 300 از 581 نتیجه یافت شده برای lb:
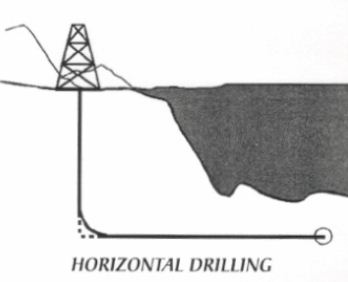
n: deviation of the borehole at least 80. from vertical so that the borehole penetrates a productive formation in a manner parallel to the formation. A single horizontal hole can effectively drain a reservoir and eliminate the need for several vertical boreholes.
n: drilling when the departure of the wellbore from vertical exceeds about 80 degrees. Beause a horizontal well typically penetrates a greater length of the reservoir, it can offer significant improvement over a vertical well.
a well drilled in a manner to reach an angle of 90 degrees relative to a level plane at its departure point at the surface. In practice, the horizontal section of most horizontal wells vary several degrees.
حفاری انحرافی
n: a kind of fishing tool that fish the broken strings in the wellbore.
لوله ی مانده گیر اصطکاکی
a diversion technique for injecting fluids into separate zones without added diverters. Limited numbers of perforations or set obstructions in the wellbore can build pressure at higher rates and cause diverting to lower permeability or damaged zones.
n: an operation in which a specially blended liquid is pumped down a well and into a formation under pressure high enough to cause the formation to crack open, forming passages through which oil can flow into the wellbore. Sand grains, aluminum pellets, glass beads, or similar materials are carried in suspension into the fractures. When the pressure is released at the surface, the fractures partially close on the proppants, leaving channels for oil to flow through to the well. Compare explosive fracturing.
n: 1.A stimulation treatment routinely performed on oil and gas wells in low-permeability reservoirs. Specially engineered fluids are pumped at high pressure and rate into the reservoir interval to be treated, causing a vertical fracture to open. The wings o
آب شکنی
the allowable effective fluid density difference between the fracturing pressure and the pressures exerted b a fluid that are needed to control formation flow and the wellbore.
adj: driven by water power. hydrofluoric acid n: a strong, poisonous liquid acid compound of hydrogen and fluorine (HF). Often mixed with hydrochloric acid, it is used mainly to remove mud from the wellbore and surrounding formation pores. Also called mud acid.
n: A number on the scale of one to 40 according to the HLB system, introduced by Griffin (1949 and 1954). The HLB system is a semi-empirical method to predict what type of surfactant properties a molecular structure will provide. The HLB system is based on t
n: (HLB) an expression of the relative attraction of an emulsifier for water and oil, determined lalgely by the chemical composition and ionisation characteristics of a given emulsifier. The HLB of an emulsifier is not directly related to solubility, but it determines the type of emulsion that tends to be formed. It is an indication of the behavioural characteristics and not an indication of emulsifier efficiency.
the pressure exerted by a column of a single density fluid. For a non-compressible fluid the pressure (in psi) at any depth = 0.052 x depth x fluid density in lb/gal.
n: the force exerted by a body of fluid at rest. It increases directly with the density and the depth of the fluid and is expressed in pounds per square inch or kilopascals. The hydrostatic pressure of fresh water is 0.433 pounds per square inch per foot (9. 792 kilopascals per metre) of depth. In drilling. the term refers to the pressure exerted by the drilling fluid in the wellbore. In a water drive field. the term refers to the pressure that may furnish the primary energy for production.
n: the load exerted by a column of fluid at rest.hydrostatic pressure increases uniformly with the density and depth of the fluid.
pressure created by a column of fluid that expresses uniform pressure in all dirrectins at a specific depth and fluid composition above the measurement point.
فشار ایستایی