نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 45 نتیجه یافت شده برای monitor:
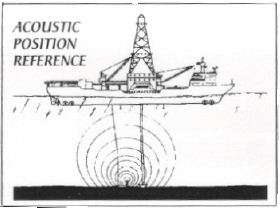
n: a system consisting of a beacon positioned on the seafloor to transmit an acoustic signal, a set of three or four hydrophones mounted on the hull of a floating offshore drilling vessel to receive the signal, and a position display unit to track the relative positions of the rig and the drill site. Monitoring of the display unit aids in accurate positioning of the rig over the site.
preset value of a monitored parameter at which an alarm is actuated to warn of a condition that requires corrective action.
مانیتور بی اس اند دبلیو
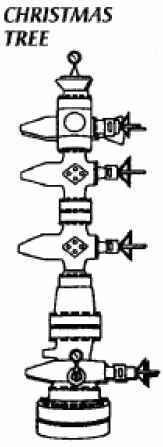
n: the conbul valves, pressure gauges, and chokes assembled at the top of a well to control the flow of oil and gas after the well has been drilled and completed. It is used when reservoir pressure is sufficient to cause reservoir fluids to flow to the surface.
n: The set of valves, spools and fittings connected to the top of a well to direct and control the flow of formation fluids from the well.
the control sections that sits above the basic wellhead. It may contain hangers, master valves, annular valves, wing valves, and gauges or pressure, flow rate or monitoring measurement equipment.
چند راهه ی فوران
n: switches and devices to start. stop, measure, monitor, or signal what is taking place.
n: a commonly used nonpolarising electrode used in corrosion control to measure the electrical potential of a metal structure to a surrounding electrolyte to determine the potential for corrosion damage or to monitor the effectiveness of existing control measures. See half-cell.
n: a metal strip inserted into a system to monitor corrosion rate and to indicate corrosion inhibitor effectiveness. corrosion fatigue n: metal fatigue concentrated in corrosion pits. See fatigue.
a representative piece of metal cut to a specific size and shape that is immersed in a test bath of placed in the flow stream to enable an estimation of the active corrosion occurring in a given set of conditions.
n: The drilling information monitoring, analysis and recording system for well site, developed by American Magcobar.
n: signals transmitted from an instrument located downhole to a receiving monitor on the surface-a surfacereadout instrument. Downhole telemetry may be transmitted via a special wireline or via mud pulse (much as radio signals are transmitted through the air). Frequently, downhole telemetry is employed in determining the drift angle and direction of a deviated wellbore. See measurement while drilling.
n: The process whereby signals are transmitted from a downhole sensor to a surface readout instrument. This can be done by a conductor line (as on steering tools) or by mud pulses (as in MWD tools (q.v.)).
n: the equipment used to supervise and control the ability,volume,flow capacity and the fluid level of the suction jar