نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 7 از 7 نتیجه یافت شده برای mud column:
n: The resistivity recorded by electrical logging. It is different from the real resistivity due to the influence of cake, invaded zone and surrounding rock.
resistivity recording where the measured value differs from the true or defined state by the influence of the mud column, invasion of a zone by fluids, or wellbore anomalies.
مقاومت ویژه ی ظاهری
n: see starting torque. break circulation v: to start the mud pump for restoring circulation of the mud column. Because the stagnant drilling fluid has thickened or gelled during the period of no circulation, high pump pressure is usually required to break circulation.
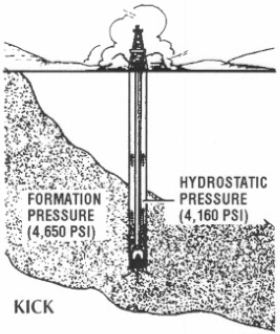
n: an entry of water, gas, oil, or other formation fluid into the wellbore during drilling. It occurs because the pressure exerted by the column of drilling fluid is not great enough to overcome the pressure exerted by the fluids in the formation drilled. If prompt action is not taken to control the kick. or kill the well, a blowout may occur. See blowout.
n/v: an entry of formation fluids (oil,gas or water) into the wellbore,caused by the formation pressure exceeding the pressure exerted by the mud column.
an unwanted flow of fluids from a formation into the wellbore. Can happen during drilling, completions or interventions.
لرزش کابل حفای
n: the borehole when it is filled or partially filled with drilling mud. mud conditioning n: the treatment and control of drilling mud to ensure that it has the correct properties. Conditioning may include the use of additives, the removal of sand or other solids, the removal of gas, the addition of water, and other measures to prepare the mud for conditions encountered in a specific well.
ستون گل حفاری
n: the pressure that the weight of mud volume enforce to the bottom of horebore.
n: the extent to which the hydrostatic pressure of the mud column exceeds formation pressure.
n: The amount of pressure (or force per unit area) in the wellbore that exceeds the pressure of fluids in the formation. This excess pressure is needed to prevent reservoir fluids (oil, gas, water) from entering the wellbore. However, excessive overbalance c
where the pressure in the wellbore in higher than the pressure in the reservoir.
n: the small amount of additional mud weight carried over that needed to balance formation pressure to overcome the pressure-reduction effects caused by swabbing when a trip out of the hole is made.
any mud density over the amount needed to balance the formation with a static mud column. Related to overbalance.