نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 10 نتیجه یافت شده برای mud pits:
v: to pass from one point throughout a system and back to me starting point. For example, drilling fluid is circulated out of the suction pit, down the drill pipe and drill collars, out the bit, up the annulus, and back to the pits while drilling proceeds.
v: To cycle drilling fluid through the drill string and wellbore, returning to the mud pits. This operation is carried out during drilling and is also used to condition the mud while drilling is suspended.
establishing flow down the tubing or drill pipe and up the annulus. Reverse circulating involves injecting down the annulus and up the drill pipe.
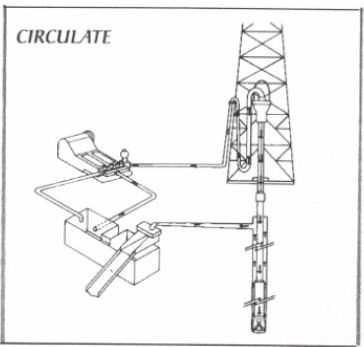
n: the movement of drilling fluid out of the mud pits, down the drill stem, up the annulus, and back to the mud pits. See normal circulation, reverse circulation.
n: The movement of drilling fluid through the flow system on a drilling or workover rig. This circulation starts at the suction pit and goes through the mud pump, drill pipe, bit, annular space in the hole, flowline, fluid pits, and back again to the suction
n: a railing for guarding against danger or trespass. On a drilling or workover rig, for example, guardrails are used on the rig floor to prevent persons from falling;guardrails are also installed on the mud pits and other high areas where there is any danger of falling.
n: 1. a hydraulic device operated by a centrifugal pump used to clean the mud pits, or tanks, and to mix mud components.2. in a perforating gun using shaped charges, a highly penetrating, fast-moving stream of exploded particles that forms a hole in the casing, cement, and formation.
n: To drill soft, unconsolidated, usually shallow formations by eroding the rock below the bit by hydraulic impact loading alone. Though not as common as in the past, a bit may be fitted with asymmetric nozzles, one large and two or more small nozzles. If
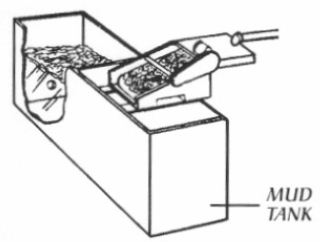
n: originally, an open pit dug in the ground to hold drilling fluid or waste materials discarded after the treatment of drilling mud. For some drilling operations, mud pits are used for suction to the mud pumps, settling of mud sediments, and storage of reserve mud. Steel tanks are much more commonly used for these purposes now, but they are still usually referred to as pits, except offshore, where mud tanks" is preferred.
the primary storage tank for drilling mud.
حوضچه ی گل درکار
n: a series of open tanks through which the mud is cycled and conditioned.modern rigs are provide with three or more pits,usually made of steel plate with built-in piping,valves and agitators.
n: one of a series of open tanks, usually made of steel plate, through which the drilling mud is cycled to remove sand and fine sediments. Additives are mixed with the mud in the tanks, and the fluid is temporarily stored there before being pumped back into the well. Modem rotary driJ1ing rigs are gen- erally provided with ~ or more tanks, fitted with txlilt-in piping, valves, and mud agitators. Also called mud pits.
n: see drilling fluid tank.
n: an instrument installed in the mud pits that has a recorder mounted on the rig floor to provide a continuous reading of the mud weight.
n: see mud density recorder.
ثبات وزن گل
n: a device that measures and records the height (level) of the drilling fluid in the mud pits. The level should remain fairly constant during the drilling of a well. If it rises. the possibility of a kick exists. Conversely. if it falls. loss of circulation may have occurred.
n: an increase in the average level of mud maintained in each of the mud pits, or tanks. If no mud or other substances have been added to the mud circulating in the well, then a pit gain is an indication that formation fluids have entered the well and that a kick has occurred.
n: when drilling belt of transition or high pressure , the fluid in layer equivalent displaces the fluid in the annular, thus arises the volume of mud pool increasing.