نمایش نتیجه 11 تا 20 از 1065 نتیجه یافت شده برای over:
v: to treat oil-bearing limestone or other formations with acid for the purpose of increasing production. Hydrochloric or other acid is injected into the formation under pressure. The acid etches the rock, enlarging the pore spaces and passages through which the reservoir fluids flow. Acid also removes formation damage by dissolving material plugging the rock surrounding the wellbore. The acid is held under pressure for a period of time and then pumped out, after which the well is swabbed and put back into production. Chemical inhibitors combined with the acid prevent corrosion of the pipe. acid recovery plant n: plant for therecovery of sulfuric acid from acid sludge.
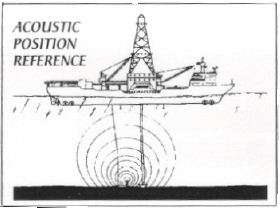
n: a system consisting of a beacon positioned on the seafloor to transmit an acoustic signal, a set of three or four hydrophones mounted on the hull of a floating offshore drilling vessel to receive the signal, and a position display unit to track the relative positions of the rig and the drill site. Monitoring of the display unit aids in accurate positioning of the rig over the site.
n: a unit of volume often used in oil reservoir analysis, equivalent to the volume (as of oil or water) necessary to cover 1 acre to a depth of 1 foot
prep: over. The term usually relates conditions of fluid flow 00 me side of a piece of equipment to conditions on the opposite side (e.g., a pressure drop across a separator).
n: (RSPA) a DOT agency that oversees the Office of Pipeline Safety, intermodal containers, highway portable tanks, railroad cars, and anything used in interstate or international commerce not regulated by the coast guard. Under OPA, RSPA has authority over onshore oil and hazardous materials pipelines that are used in interstate commerce. Address: 400 7th Street SW;Washington, DC 20590;(202) 366-4433.
n: the adhesion of a thin film of a gas or liquid to the surface of a solid. Liquid hydrocarbons are recovered from natural gas by passing the gas through activated charcoal, silica gel, or other solids, which extract the heavier hydrocarbons. Steam treatment of the solid removes the adsorbed hydrocarbons, which are then collected and re-condensed. The adsorption process is also used to remove water vapour from air or natural gas. Compare absorption.
n: A surface phenomenon exhibited by a solid (adsorbent) to hold or concentrate gases, liquids or dissolved substances(adsorptive) upon its surface, due to adhesion.
the attraction and holding of a layer of a chemical on the wall of a formation. Usually held by ionic charge or wetting preference.
n: a fog caused by the movement of warm, moist air over a surface with a temperature less than the dew point of the air. Also called sea fog.
n: a method of asserting and gaining title to property against other claimants, including the owner of record. The claim through adverse possession must include certain acts (as required by statute) over an uninterrupted interval of time. It must also be, in most states, open," "notorious," and "hostile."
n: see air-cooled exchanger. aerial river crossing n: a river crossing technique in which a pipeline is either suspended by cables over a waterway or attached to the girders of a bridge designed to carry vehicular traffic.
Authority for Expenditure on a well (authorized funds for drilling or workover).