نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 41 نتیجه یافت شده برای peat:
n: A method of cementing. Put a stop means below the section of cementing, fill the tailored slurry in the bailer, land to the desired location, open the bailer and make slurry in the well. Repeat the process till all slurry poured into the well.
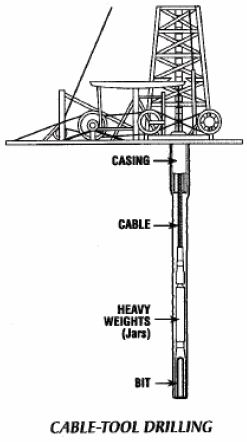
n: a drilling method in which the hole is drilled by the rigs equipment dropping a sharply pointed and heavily weighted bit on bottom. The bit and weight are attached to a cable, and the rigs equipment repeatedly drops the cable to drill the hole.
n: Theuseful life of a coiled tubing work string is limited due to fatigue damage. This damage is caused by the repeated bending and straightening of the coiled tubing at the gooseneck and reel. The resulting failure mechanism is referred to an low cycle fat
n: The stress corrosion of metal. Produced by the affect of strees and corrosive media.
fatigue-type cracking of metal caused by repeated stresses in a corrosive environment.
خستگی خوردگی
a mineral with a systematic internal arrangement of ions that forms a repeating outward latticework of three dimentional units.
n: the injection of steam into the rock surrounding a production well to lower the viscosity of heavy oil and increase its flow into the wellbore. Steam injection may be followed by immediate production or by closing the well (called the soak phase) to allow even heat distribution before production is begun. The cycle of injection, soak, and production is repeated as long as the oil yield is profitable. Also called steam soak and huff n puff.
n: carcinogens and other hazardous chemicals that cause an adverse effect on a target organ (as defined by the Code of Federal Regulations) that manifests itself after a long period of time following or during repeated contact with the substance.
n: Repeat this process as follow:inject quantitative drill fluid into the well,and then shut down the well to make sure the fluid get to the bottom ,and at last release quantitative pressure.
n: the closeness of the agreement between the results of successive measurements of the same quantity carried out by the same method, under the same environment, by the same observer, with the same measuring instruments, in the same laboratory, at quite short intervals.
n: the tendency of material such as a metal to break under repeated cyclic loading at a stress considerably less than the tensile strength shown in a static test.
a metal failure based on weakening by flexing or cycling. The material often work hardens.