نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 14 نتیجه یافت شده برای producing zone:
n: a test that measures the reservoir pressure of the well, obtained at a specific depth or at the midpoint of the producing zone. A flowing bottomhole pressure test measures pressure while the well continues to flow;a shut-in bottomhole pressure test measures pressure after the well has been shut in for a specified period of time. See bottomhole pressure. bottomhole pressure gauge.
n: temperature measured in a well at a depth at the midpoint of the thickness of the producing zone.
n: a variation of squeeze cementing for wells with two producing zones in which (1) the upper fluid sand is perforated;(2) tubing is run with a packer, and the packer is set between the two perforated intervals;(3) water is circulated between the two zones to remove as much mud as possible from the channel;(4) cement is pumped through the channel and circulated;(5) the packer is released and picked up above the upper perforation, a low squeeze pressure is applied, and the excess cement is circulated out. The process is applicable where there is communication behind the pipe between the two producing zones because of channelling of the primary cement or where there is essentially no cement in the annulus.
a secondary or repair cement method using upper and lower perforations and a packer set between. Circulation is established with water and mud remover chemicals to clean the channel. Cement is circulated with a set volume pumped, then the packer is releas
n pi: a classification of injection wells under SDWA that are related to oil and gas activity. Typically, these wells are used to dispose of produced waters into depleted oil formations below drinking water sources;to inject produced water from production operations back into the producing zone;to inject fluids for enhanced recovery;and to store hydrocarbons.
n: the pressure at a given temperature for a hydrocarbon system of fixed composition at which the vapourliquid equilibrium values of the various components in the system become or tend to become unified. The convergence pressure is used to adjust vapour-liquid equilibrium values to the particular system under consideration. conversion n: the change in the chemistry of a mud from one type to another. Reasons for making a conversion may be (1) to maintain a stable well bore, (2) to provide a mud that will tolerate higher weight, or density, (3) to drill soluble formations, or (4) to protect producing zones. Also called a breakover.
n: a drilling fluid specially formulated to minimize formation damage as the borehole penetrates the producing zone. See formation damage. Compare completion fluid.
the fluid used to drill the pay zone.
n: a fracturing method in which fracturing fluid is injected into the formation through a limited number of perforations (i.e., fluid is not injected through all the perforations at once;rather, injection is confined to a few selected perforations). This special technique can be useful when long, thick, or multiple producing zones are to be fractured.
n: 1. the last string of casing set in a well. 2. the string of casing that is set at the top of or through the producing zone, often called the oil string or production casing.
in a side-by-side dual completion, the tubing string that connects the deeper zone to the surface.
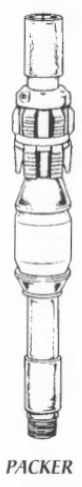
n: a piece of downhole equipment that consists of a sealing device, a holding or setting device. and an inside passage for fluids. It is used to block the flow of fluids through the annular space between pipe and the wall of the wellbore by sealing off the space between them. In production, it is usually made up in the tubing string some distance above the producing zone. A packing element expands to prevent fluid flow except through the packer and tubing. Packers are classified according to configuration, use, and method of setting and whether or not they are retrievable (that is, whether they can be removed when necessary, or whether they must be milled or drilled out and thus destroyed).
n: a downhole tool, run on drill pipe, tubing or casing, which can be used extensively in drill stem tests, cement squeezes and complections.
a device that forms a seal between two chambers of the well. Packers may be equipped with slips that anchors the packer and stops movement under high pressure.
توپک
n: the producing formation, often one that is not even sandstone. Also called pay, pay zone, and producing zone. pay string n: see production casing.
n: the layer that presents industry working value, not limited sand rock.