نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 14 نتیجه یافت شده برای tectonic:
n: a reef or mound built by small organisms and their remains, such as coral, plankton, and oysters. Originally a waveresistant coral structure served as an anchor for calcareous debris that formed limestone. It was tectonically submerged, or the sea level rose faster than the corals could build it, and it was eventually buried beneath marine shales. A bioherm is often porous enough to hold large accumulations of hydrocarbons, especially if it has been dolomitized. A bioherm is a stratigraphic trap.
powdered rock created by crushing and shearing of tectonic movements.
n: according to a theory proposed by Alfred Wegener, a German meteorologist, in 1910, the migration of continents across the ocean floor like rafts drifting at sea. Compare plate tectonics.
the stresses on the formation imposed by the overlying overburden and tectonic forces. The stresses are at least partially offset by the fluids in the pores of the formation.
the small energy emissions from small feature tectonic events, including production of fluids from a reservoir and the resultant transfer of overburden to the matrix of the reservoir.
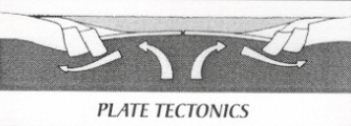
n pi: movement of great crustal plates of the earth on slow currents in the plastic mantle, similar to the movement of boxes on a conveyor belt. Today geologists believe that the earths crust is divided into six major plates and several smaller ones atop some of which the continents are carried away from a system of mklocean ridges and toward another system of deep-sea trenches. The theory of plate tectonics explains most of the mysteries that confounded earlier geologists. Compare continental drift.
لایه طبقات زمین شناسی
n: a type of metamorphism that occurs in bodies of rock that have been deeply buried or greatly defonned by tectonic changes.
“shock” waves from an event (explosive, tectonic, impact, etc.) that travel through the earth and reflect off of subsurface structures (rocks) in the same manner as sound echos and water waves and ripples.
n: The shale collapsed caused by hydration,erosion,high pressure and tectonic stress.
a shale, usually in the wellbore, that increases size (swells) or casts of particles by reacting with brine or water.
a tectonically induced failure of a section of a formation with the result that one block of the formation moves horizontally to the formation.