نمایش نتیجه 1 تا 10 از 102 نتیجه یافت شده برای workover:
Authority for Expenditure on a well (authorized funds for drilling or workover).
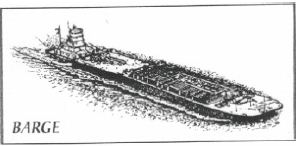
n: 1. a flat-decked, shallow-draft vessel, usually towed by a boat. Barges are not self-propelled. They are used to transport oil or products on rivers, lakes, and inland waterways. Also, a complete drilling rig may be assembled on a barge and the vessel used for drilling wells in lakes and in inland waters and marshes. Similarly, well service and workover equipment can be mounted on a barge. 2. an offshore drilling vessel built in the shape of a ship. Unlike a ship, however, it is not self-propelled. Also called a drill barge.
marine vessel without its own propulsion.
دوبه
a conditional surface pressure barrier often consisting of a set of hydraulically operated rams containing equipment designed to grip pipe, seal around pipe, shear off pipe or seal an open hole during drilling or a workover. It may also contain an annular
The pressure at the bottom of the well. In a producing well the BHP may be the bottom hole flowing pressure or the bottom hole shut-in pressure. In a drilling or workover environment, the BHP is exerted by the column of fluid in the hole.
n: the apparent loss of weight of an object immersed in a fluid. If the object is floating, the immersed portion displaces a volume of fluid the weight of which is equal to the weight of the object.
n: The upward force acting on an object placed in a fluid. The buoyancy force is equal to the weight of fluid displaced by the object. Buoyancy can have significant effects over a wide range of completion and workover activities, especially in cases in which
the amount of weight that is offset by lift from the fluid when the piece of equipment is immersed in the fluid.
n: a moisture-absorbing chemical compound, or desiccant, CaCI2, used to accelerate setting times in cement and as a drying agent. It is also added to fresh water to increase the waters weight and to give it desirable properties during well completion or workover.
n: CaCl2, a kind of absorption chemical compound.Usually used for calcium mud and heavy weight additive of completion fluid.
CaCl2, a water soluble brine weighting agent.
کلرور کلسیم
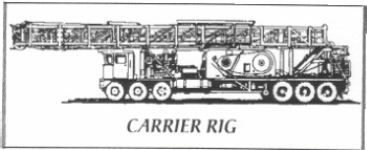
n: a large, specially designed, self-propelled workover rig that is driven directly to the well site. Power from a carrier rigs hoist engine or engines also propels the rig on the road. While a carrier rig is primarily intended to perform workovers, it can also be used to drill relatively shallow wells. A carrier rig may be a back-in type or a drive-in type. Compare back-in unit, drive-in unit.
n: A kind of portable service machine. The derrick mask, drawworks, motor and other necessary additional service rig.
a self propelled drilling or workover rig.
ریگ سیار
n: a pipe attached to the blowout preventer stack out of which kick fluids and mud can be pumped to the choke manifold when a blowout preventer is closed in on a kick.
n: A high-pressure pipe leading from an outlet on the BOP stack to the backpressure choke and associated manifold. During well-control operations, the fluid under pressure in the wellbore flows out of the well through the choke line to the choke, reducing th
a drilling and workover pressure control device. A line that attached to the BOP stack and through which kick fluids can be circulated when the BOP is closed.
n: the movement of drilling fluid out of the mud pits, down the drill stem, up the annulus, and back to the mud pits. See normal circulation, reverse circulation.
n: The movement of drilling fluid through the flow system on a drilling or workover rig. This circulation starts at the suction pit and goes through the mud pump, drill pipe, bit, annular space in the hole, flowline, fluid pits, and back again to the suction
n: Consisted by car-borne reciprocal pump. Used for workover. For example, sand washing and flushing.